LeetCode 212:给定一个 m x n 二维字符网格 board 和一个单词(字符串)列表 words,找出所有同时在二维网格和字典中出现的单词。
单词必须按照字母顺序,通过 相邻的单元格 内的字母构成,其中“相邻”单元格是那些水平相邻或垂直相邻的单元格。同一个单元格内的字母在一个单词中不允许被重复使用。
示例:
![]()
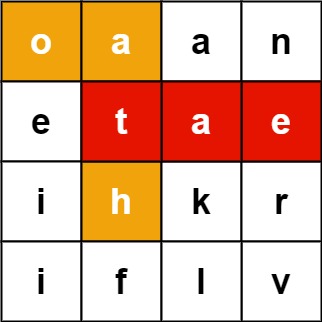
- 输入:board = [[“o”,“a”,“a”,“n”],[“e”,“t”,“a”,“e”],[“i”,“h”,“k”,“r”],[“i”,“f”,“l”,“v”]], words = [“oath”,“pea”,“eat”,“rain”]
- 输出:[“eat”,“oath”]
思路
- 将 words 构建成 Trie 树,加快用于后面的匹配过程
- 从每个单元格开始,如果字典中存在以单元格中的字母开头的单词,则我们开始回溯探索,即
backtrack(cell)
- 在递归函数
backtracking(cell) 调用过程中,我们探索当前单元格周围的相邻单元格(即 neighborCell)以进行下一个递归调用 backtracking(neighborCell)。在每次调用时,我们都会检查到目前为止遍历的字母序列是否与字典中的任何单词匹配,这需要借助于我们在开始时构建的 Trie 数据结构。
优化
源码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
| int n, m;
char[][] board;
TrieNode root;
List<String> ans = new ArrayList<>();
int[] rowOffset = {-1, 0, 1, 0};
int[] colOffset = {0, 1, 0, -1};
public List<String> findWords(char[][] board, String[] words) {
this.n = board.length;
this.m = board[0].length;
this.board = board;
root = new TrieNode();
for (String word : words) {
TrieNode node = root;
for (char ch : word.toCharArray()) {
if (node.children.containsKey(ch)) {
node = node.children.get(ch);
} else {
TrieNode newNode = new TrieNode();
node.children.put(ch, newNode);
node = newNode;
}
}
node.word = word;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (root.children.containsKey(board[i][j])) {
backtrack(i, j, root);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
public void backtrack(int row, int col, TrieNode node) {
char letter = board[row][col];
TrieNode curNode = node.children.get(letter);
if (curNode.word != null) {
ans.add(curNode.word);
curNode.word = null;
return;
}
board[row][col] = '#';
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int newRow = row + rowOffset[i];
int newCol = col + colOffset[i];
if (newRow < 0 || newRow >= n || newCol < 0 || newCol > m) {
continue;
}
if (curNode.children.containsKey(board[newRow][newCol])) {
backtrack(newRow, newCol, curNode);
}
}
board[row][col] = letter;
if (curNode.children.isEmpty()) {
node.children.remove(letter);
}
}
class TrieNode {
HashMap<Character, TrieNode> children;
String word;
public TrieNode() {
children = new HashMap<>();
word = null;
}
}
|